Dimitri Mendeleev first created the periodic table in the year 1869. He started to put together what we now know as the Modern Periodic Table as a puzzle. All the elements were not discovered back then, and Mendeleev assumed that some were missing.
Learning the First 20 Elements with Symbols is a must. The periodic table follows certain trends regarding atomic size and atomic weight and is arranged according to the trends.
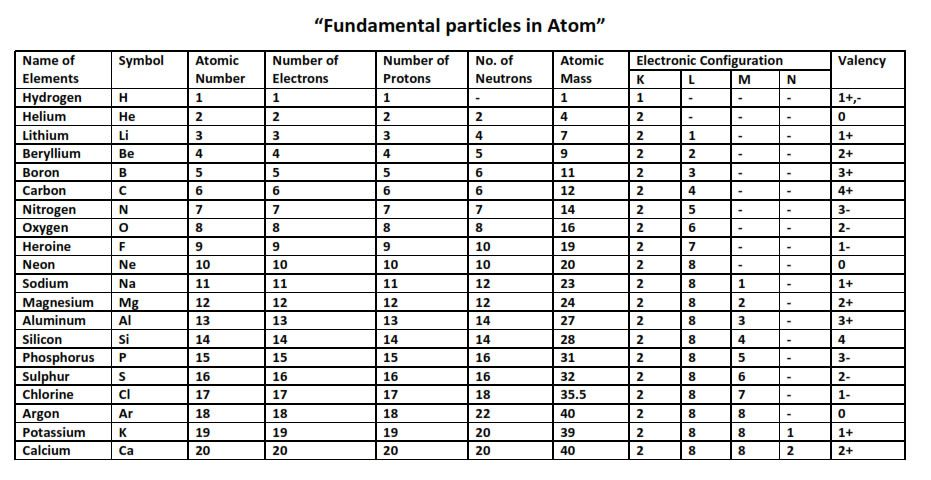
The first twenty elements of the periodic table are as following along with their symbols –
- Hydrogen (H1) – It is gaseous. This is a nonmetal with atomic number 1; hydrogen is an essential element for the very existence of life itself. Without hydrogen, organic compounds would not be formed. It is used as a fuel for rockets, welding and plays a crucial role in the industrial formation of ammonia by the Haeber’s process. It is envisioned as the future of clean fuel for electric cars.
- Helium (He2) – It is gaseous. It is a noble gas and has an atomic number 2. Due to its inert properties, it is used for making fibre optics and semiconductors. It has a high rate of diffusion and is therefore used to fill up car airbags after impact.
- Lithium (Li3) – It is solid. It is an alkaline metal with atomic number 3. Lithium has the highest specific heat capacity and is the lightest known metal. Therefore, it is used to make special glasses and ceramics, can be used as an alloy with copper, aluminium, etc., to make strong but lightweight metal for aircraft.
- Beryllium (Be4) – It is solid. It is an alkaline earth metal with atomic number 4. It is quite soft with low density, it is used in making springs, gyroscopes, and gears and cogs of the aviation industry.
- Boron (B5) – It is solid. It is a metalloid with the atomic number 5. Compounds of boron like sodium borate (borax) and boric acid have multiple important uses because of their mild antiseptics. They are used in washing powders, eye drops and tile glazes.
- Carbon (C6) – It is solid. It is a nonmetal with the atomic number 6. It is the most important element in making organic compounds and forms 18% of the human body. When carbon is found in its diamond form, it is found in jewellery.
- Nitrogen (N7) – It is gaseous. It is a nonmetal with the atomic number 6. It plays a major role in making DNA and RNA, and nucleic acids by forming nitrogenous bases. It is also a component of protein, nucleic acid, and other organic compounds that help form amino acids and make proteins.
- Oxygen (O8) – It is gaseous. It is a nonmetal with the atomic number 8. Oxygen is crucial for anaerobic mode of respirations in cells, and in its liquid form, oxygen is used as an oxidising agent in fuels like rockets and missiles.
- Fluorine (F9) – It is gaseous in nature. It is a halogen with the atomic number 9. Fluorine is used to produce nuclear material at nuclear power plants and in combination with hydrogen as hydrogen fluoride to etch glass. Fluorine also plays a role in dental health.
- Neon (Ne10) – it is gaseous in nature. It is a noble gas with the atomic number 10. It is used to make lightning arresters, diving equipment, lasers and in its liquid form, a cryogenic refrigerant.
- Sodium (Na11) – it is solid in nature. It is an alkali metal with the atomic number 11. It is sodium in salt with more uses than common salt (NaCl, sodium chloride). However, liquid sodium is used as a coolant (heat exchanger) in nuclear reactors.
- Magnesium (Mg12) – It is solid. It is an alkali metal with the atomic number 12. Magnesium plays an important role in human metabolism and also in plants in the chlorophyll molecule.
- Aluminium (Al13) – it is solid in nature. It is an alkaline earth metal with atomic number 13. As a good conductor of electricity, it is often a good replacement for copper in electrical transmission. They are used in making aeroplanes.
- Silicon (Si14) – This solid metalloid has the atomic number of 14. It is used in the production of alloys to make cylinder heads, engine blocks and dynamos.
- Phosphorus (P15) – This solid nonmetal has an atomic number of 15. It is needed to form good bones and teeth.
- Sulfur (S16) – it is solid in nature. It is a nonmetal with the atomic number 16. It forms two of the essential amino acids and is needed as coenzymes in the body.
- Chlorine (Cl17) – is gaseous. It is a halogen gas with the atomic number 17. it performs as a disinfectant, killing bacteria and treating drinking water and swimming pools.
- Argon (Ar18) – it is gaseous in nature. It is a noble gas with the atomic number 18. Its inertness makes it suitable to prevent oxygen corrosion in incandescent bulbs and the production of reactive elements like titanium.
- Potassium (K19) – it is solid in nature. It is an alkali metal with the atomic number 19. It is a needed component for the working of the human system. It aids nerve signals transmissions, fluid balance in the body by Na/K channels and treats high blood pressure levels.
- Calcium (Ca20) – It is solid. It is an alkaline earth metal with atomic number 20. It is important for humans for maintaining healthy teeth and bones. It is also used to make plaster of Paris.
Conclusion
Learning the periodic table by heart is recommended because it forms the basis of chemistry and chemical learning. The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) controls the elements to be added and changes to be made as and when required in the Modern Periodic Table.